ESP8266 Audio Decoding
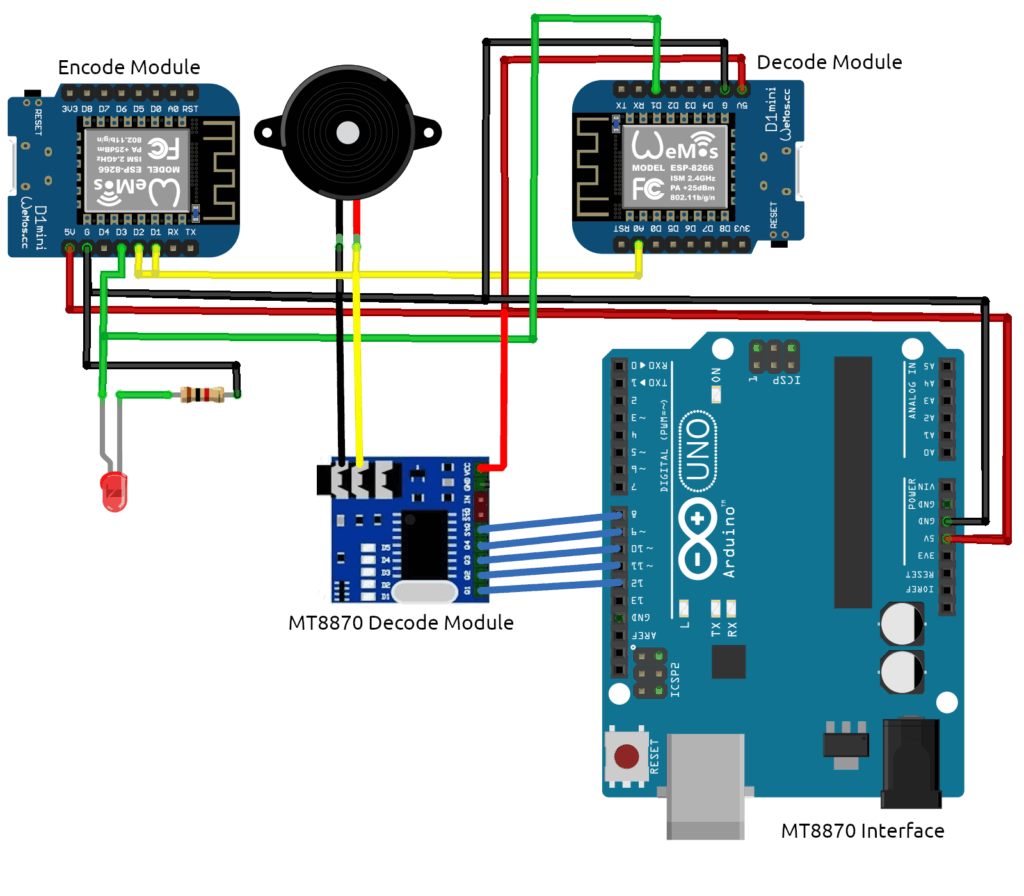
In the last post, I covered how to generate audio natively with the ESP8266 module. The hardware to do this is rudimentary. I demonstrated how to generate CW (Morse Code), DTMF, synthesized speech, and audio. This post will expand on some of those concepts by decoding CW and DTMF signals. The following Fritzing wiring diagram will be the foundation for all of the code covered in this post.
The Encode Module will be the signal source for the Decoding modules. I’ve included a MT8870 Decode module as well as an Arduino Uno to highlight the simplicity of the ESP8266 Decode module.
For the first demonstration, I’ll cover CW signaling (Morse Code). The Encode Module code is as follows and is similar to what was provided in an earlier post. I do want to point out that the timing of the encoder and decode modules need to match. I’m using a 35ms timing base for the dot and gap duration. Dashes, letter gaps, and word gaps use standard 3, 3, and 7 multiples respectively.
int SignalPin = 0; // D3 on NodeMCU GPIO0
int unit = 35; // base time unit in ms
int dot = unit;
int dash = 3 * unit;
int gap = unit; // between elements
int letterGap = 3 * unit; // between letters
int wordGap = 7 * unit; // between words
// ---- Helpers ----
void playDot() {
digitalWrite(SignalPin, HIGH);
delay(dot);
digitalWrite(SignalPin, LOW);
delay(gap);
}
void playDash() {
digitalWrite(SignalPin, HIGH);
delay(dash);
digitalWrite(SignalPin, LOW);
delay(gap);
}
// ---- Morse Table ----
struct MorseMap {
char letter;
const char *pattern;
};
MorseMap morseTable[] = {
// Letters
{'A', ".-"}, {'B', "-..."}, {'C', "-.-."}, {'D', "-.."},
{'E', "."}, {'F', "..-."}, {'G', "--."}, {'H', "...."},
{'I', ".."}, {'J', ".---"}, {'K', "-.-"}, {'L', ".-.."},
{'M', "--"}, {'N', "-."}, {'O', "---"}, {'P', ".--."},
{'Q', "--.-"}, {'R', ".-."}, {'S', "..."}, {'T', "-"},
{'U', "..-"}, {'V', "...-"}, {'W', ".--"}, {'X', "-..-"},
{'Y', "-.--"}, {'Z', "--.."},
// Digits
{'0', "-----"}, {'1', ".----"}, {'2', "..---"},
{'3', "...--"}, {'4', "....-"}, {'5', "....."},
{'6', "-...."}, {'7', "--..."}, {'8', "---.."},
{'9', "----."},
// Punctuation
{'.', ".-.-.-"}, {',', "--..--"}, {'?', "..--.."}, {'\'', ".----."},
{'!', "-.-.--"}, {'/', "-..-."}, {'(', "-.--."}, {')', "-.--.-"},
{'&', ".-..."}, {':', "---..."}, {';', "-.-.-."}, {'=', "-...-"},
{'+', ".-.-."}, {'-', "-....-"}, {'_', "..--.-"}, {'\"', ".-..-."},
{'$', "...-..-"},{'@', ".--.-."}
};
int tableSize = sizeof(morseTable) / sizeof(MorseMap);
// ---- Play one letter ----
void playLetter(char c) {
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') c -= 32; // uppercase
// find in table
for (int i = 0; i < tableSize; i++) {
if (morseTable[i].letter == c) {
const char *p = morseTable[i].pattern;
while (*p) {
if (*p == '.') playDot();
else if (*p == '-') playDash();
p++;
}
delay(letterGap - gap); // inter-letter spacing
return;
}
}
if (c == ' ') {
delay(wordGap); // word gap
}
}
// ---- Play a full message ----
void playMessage(const char *msg) {
while (*msg) {
playLetter(*msg);
msg++;
}
}
void setup() {
pinMode(SignalPin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SignalPin, LOW);
}
void loop() {
playMessage("However difficult life may seem, there is always something you can do and succeed at.");
delay(2000);
playMessage("Remember to look up at the stars and not down at your feet.");
delay(10000);
}
The Decode Module code is as follows. It outputs the decoded Morse code to the serial monitor.
const uint8_t telegraphPin = 5; // D1 on NodeMCU = GPIO5
bool telegraphActive = false;
bool telegraphWasPressed = false;
unsigned long pulseStartTime = 0;
unsigned long pulseEndTime = 0;
// timing units (ms)
const int unit = 35;
const int dotThresh = unit; // ≤1 unit ⇒ dot
const int dashThresh = 3 * unit; // ≤3 units ⇒ dash
const int letterGap = 3 * unit; // ≥3 units ⇒ new letter
const int wordGap = 7 * unit; // ≥7 units ⇒ new word
String codeBuffer = "";
// full map: letter, digit, and period
struct MorseMap {
const char *pattern;
char decoded;
};
MorseMap table[] = {
// Letters
{".-", 'A'}, {"-...", 'B'}, {"-.-.", 'C'}, {"-..", 'D'},
{".", 'E'}, {"..-.", 'F'}, {"--.", 'G'}, {"....", 'H'},
{"..", 'I'}, {".---", 'J'}, {"-.-", 'K'}, {".-..", 'L'},
{"--", 'M'}, {"-.", 'N'}, {"---", 'O'}, {".--.", 'P'},
{"--.-", 'Q'}, {".-.", 'R'}, {"...", 'S'}, {"-", 'T'},
{"..-", 'U'}, {"...-", 'V'}, {".--", 'W'}, {"-..-", 'X'},
{"-.--", 'Y'}, {"--..", 'Z'},
// Digits
{"-----", '0'}, {".----", '1'}, {"..---", '2'}, {"...--", '3'},
{"....-", '4'}, {".....", '5'}, {"-....", '6'}, {"--...", '7'},
{"---..", '8'}, {"----.", '9'},
// Punctuation
{".-.-.-", '.'}, {"--..--", ','}, {"..--..", '?'}, {".----.", '\''},
{"-.-.--", '!'}, {"-..-.", '/'}, {"-.--.", '('}, {"-.--.-", ')'},
{".-...", '&'}, {"---...", ':'}, {"-.-.-.", ';'}, {"-...-", '='},
{".-.-.", '+'}, {"-....-", '-'}, {"..--.-", '_'}, {".-..-.", '\"'},
{"...-..-", '$'}, {".--.-.", '@'}
};
const int tableSize = sizeof(table) / sizeof(MorseMap);
void setup() {
pinMode(telegraphPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
int state = digitalRead(telegraphPin);
// ——— Key down ⇒ start measuring “on” pulse ———
if (state == HIGH) {
if (!telegraphActive) {
telegraphActive = true;
telegraphWasPressed = false;
pulseStartTime = millis();
}
return;
}
// ——— Key up ⇒ end of pulse ⇒ classify dot/dash ———
if (telegraphActive) {
telegraphActive = false;
pulseEndTime = millis();
unsigned long onLen = pulseEndTime - pulseStartTime;
if (onLen >= dotThresh) {
// dot or dash?
if (onLen < dashThresh) codeBuffer += '.';
else codeBuffer += '-';
telegraphWasPressed = true;
}
return;
}
// ——— After a pulse, watch for gap ⇒ letter or word boundary ———
if (telegraphWasPressed) {
unsigned long offLen = millis() - pulseEndTime;
// letter gap (just over 3 units)
if (offLen >= letterGap && offLen < wordGap) {
decodeAndPrint(codeBuffer);
codeBuffer = "";
telegraphWasPressed = false;
}
// word gap (7 units)
else if (offLen >= wordGap) {
decodeAndPrint(codeBuffer);
codeBuffer = "";
Serial.print(' ');
telegraphWasPressed = false;
}
}
}
// ——— Lookup and print one symbol ———
void decodeAndPrint(const String &code) {
for (int i = 0; i < tableSize; i++) {
if (code == table[i].pattern) {
Serial.print(table[i].decoded);
return;
}
}
// if not found:
Serial.print('?');
}
I modified the Encoder Module code to allow detection from signal state or tone sensing devices.
int SignalPin = 0; // D3 on NodeMCU GPIO0
int TonePin = 5; // D1 on NodeMCU GPIO5
int freq = 1000; // Hz
int unit = 35; // base time unit in ms
int dot = unit;
int dash = 3 * unit;
int gap = unit; // between elements
int letterGap = 3 * unit; // between letters
int wordGap = 7 * unit; // between words
// ---- Helpers ----
void playDot() {
digitalWrite(SignalPin, HIGH);
tone(TonePin, freq);
delay(dot);
digitalWrite(SignalPin, LOW);
noTone(TonePin);
delay(gap);
}
void playDash() {
digitalWrite(SignalPin, HIGH);
tone(TonePin, freq);
delay(dash);
digitalWrite(SignalPin, LOW);
noTone(TonePin);
delay(gap);
}
// ---- Morse Table ----
struct MorseMap {
char letter;
const char *pattern;
};
MorseMap morseTable[] = {
// Letters
{'A', ".-"}, {'B', "-..."}, {'C', "-.-."}, {'D', "-.."},
{'E', "."}, {'F', "..-."}, {'G', "--."}, {'H', "...."},
{'I', ".."}, {'J', ".---"}, {'K', "-.-"}, {'L', ".-.."},
{'M', "--"}, {'N', "-."}, {'O', "---"}, {'P', ".--."},
{'Q', "--.-"}, {'R', ".-."}, {'S', "..."}, {'T', "-"},
{'U', "..-"}, {'V', "...-"}, {'W', ".--"}, {'X', "-..-"},
{'Y', "-.--"}, {'Z', "--.."},
// Digits
{'0', "-----"}, {'1', ".----"}, {'2', "..---"},
{'3', "...--"}, {'4', "....-"}, {'5', "....."},
{'6', "-...."}, {'7', "--..."}, {'8', "---.."},
{'9', "----."},
// Punctuation
{'.', ".-.-.-"}, {',', "--..--"}, {'?', "..--.."}, {'\'', ".----."},
{'!', "-.-.--"}, {'/', "-..-."}, {'(', "-.--."}, {')', "-.--.-"},
{'&', ".-..."}, {':', "---..."}, {';', "-.-.-."}, {'=', "-...-"},
{'+', ".-.-."}, {'-', "-....-"}, {'_', "..--.-"}, {'\"', ".-..-."},
{'$', "...-..-"},{'@', ".--.-."}
};
int tableSize = sizeof(morseTable) / sizeof(MorseMap);
// ---- Play one letter ----
void playLetter(char c) {
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') c -= 32; // uppercase
// find in table
for (int i = 0; i < tableSize; i++) {
if (morseTable[i].letter == c) {
const char *p = morseTable[i].pattern;
while (*p) {
if (*p == '.') playDot();
else if (*p == '-') playDash();
p++;
}
delay(letterGap - gap); // inter-letter spacing
return;
}
}
if (c == ' ') {
delay(wordGap); // word gap
}
}
// ---- Play a full message ----
void playMessage(const char *msg) {
while (*msg) {
playLetter(*msg);
msg++;
}
}
void setup() {
pinMode(SignalPin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SignalPin, LOW);
}
void loop() {
playMessage("However difficult life may seem, there is always something you can do and succeed at.");
delay(2000);
playMessage("Remember to look up at the stars and not down at your feet.");
delay(10000);
}
The DTMF Encoding was done with this code. I decided to change up the typical 0-9, A-D, * and # for a hexidecimal range instead. It replaces E for * and F for #. I wanted to see if I could decode a hex dump of the song “A Mind Is Born” from Linus Akesson.
/*
A sketch to demonstrate the tone() function with a character‐map and PlayTone()
This is a hex dump of "A Mind Is Born" (xxd -p a_mind_is_born.prg), https://linusakesson.net/scene/a-mind-is-born/
Based on a 4 x 4 keypad membrane, 0-9, A-D, * and #
* represents E and # represents F
01080D08##D39*323232350000001941
1CD000DC000011D0*00B10330*6190#5
0700##1#1441D524152515531561D529
1B0#*613*613D002*620A961851CA720
*03##008900C4*11D06C#C##A06D8422
84D74A4B1CA8A5132930D002C61C*02#
#011B002A202C910#0098A2903AAB5#3
850A2DAB00B011B722B6219500A5134B
0*AACB#886CC4907850BA513290#D00#
A9B84714900285142907AAB5#78512A0
08B70D910#8810#9A8B709910388D0#9
4C7**A788*86028*21D02044*5A2#DBD
02089502CAD0#88*15034CCC00A9508D
11D058AD04DCA0C30D1CD4484B04A030
8C18D071CB*6CB71CB6A0520A05805D5
91CBD0D#2BAA02620018262012241310
*/
// Specify pins that lead to positive terminal of piezo buzzer.
const int LoTone = 5; // GPIO5 - D1
const int HiTone = 4; // GPIO4 - D2
// Durations
const int OnDuration = 50;
const int OffDuration = OnDuration * 2;
// DTMF frequencies
const int LoFreq1 = 697;
const int LoFreq2 = 770;
const int LoFreq3 = 852;
const int LoFreq4 = 941;
const int HiFreq1 = 1209;
const int HiFreq2 = 1336;
const int HiFreq3 = 1477;
const int HiFreq4 = 1633;
// Keypad layout: 1 2 3 A
// 4 5 6 B
// 7 8 9 C
// * 0 # D
const char mapKeys[] = "123A456B789C*0#D";
// Parallel frequency arrays for quick lookup
const int loFreqMap[16] = {
LoFreq1, LoFreq1, LoFreq1, LoFreq1,
LoFreq2, LoFreq2, LoFreq2, LoFreq2,
LoFreq3, LoFreq3, LoFreq3, LoFreq3,
LoFreq4, LoFreq4, LoFreq4, LoFreq4
};
const int hiFreqMap[16] = {
HiFreq1, HiFreq2, HiFreq3, HiFreq4,
HiFreq1, HiFreq2, HiFreq3, HiFreq4,
HiFreq1, HiFreq2, HiFreq3, HiFreq4,
HiFreq1, HiFreq2, HiFreq3, HiFreq4
};
// Play a sequence of DTMF characters
void PlayTone(const char* seq) {
for (int i = 0; seq[i] != '\0'; ++i) {
// find index in mapKeys
const char c = seq[i];
char* p = (char*)strchr(mapKeys, c);
if (p != nullptr) {
int idx = p - mapKeys;
tone(LoTone, loFreqMap[idx], OnDuration);
tone(HiTone, hiFreqMap[idx], OnDuration);
}
// pause between tones
delay(OffDuration);
}
}
void setup() {
pinMode(LoTone, OUTPUT);
pinMode(HiTone, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// define your DTMF string here
PlayTone("01080D08##D39*323232350000001941");
PlayTone("1CD000DC000011D0*00B10330*6190#5");
PlayTone("0700##1#1441D524152515531561D529");
PlayTone("1B0#*613*613D002*620A961851CA720");
PlayTone("*03##008900C4*11D06C#C##A06D8422");
PlayTone("84D74A4B1CA8A5132930D002C61C*02#");
PlayTone("#011B002A202C910#0098A2903AAB5#3");
PlayTone("850A2DAB00B011B722B6219500A5134B");
PlayTone("0*AACB#886CC4907850BA513290#D00#");
PlayTone("A9B84714900285142907AAB5#78512A0");
PlayTone("08B70D910#8810#9A8B709910388D0#9");
PlayTone("4C7**A788*86028*21D02044*5A2#DBD");
PlayTone("02089502CAD0#88*15034CCC00A9508D");
PlayTone("11D058AD04DCA0C30D1CD4484B04A030");
PlayTone("8C18D071CB*6CB71CB6A0520A05805D5");
PlayTone("91CBD0D#2BAA02620018262012241310");
// wait before repeating (optional)
delay(60000);
}
Here is the DTMF Decoding Module code.
#include <Arduino.h>
// sample parameters
const uint16_t SAMPLE_RATE = 8000; // Hz
const uint16_t N = 205; // samples per block (~25.6 ms)
// Goertzel target frequencies
const float freqsLow[4] = { 697.0, 770.0, 852.0, 941.0 };
const float freqsHigh[4] = {1209.0,1336.0,1477.0,1633.0 };
// Goertzel state arrays
float coeffsLow[4], coeffsHigh[4];
float sLow_prev[4], sLow_prev2[4];
float sHigh_prev[4], sHigh_prev2[4];
// mapping row/col to digit
const char dtmfMap[4][4] = {
{ '1','2','3','A' },
{ '4','5','6','B' },
{ '7','8','9','C' },
{ 'E','0','F','D' }
};
char lastDigit = '\0';
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
float ωL = 2.0 * PI * freqsLow[i] / SAMPLE_RATE;
coeffsLow[i] = 2.0 * cos(ωL);
float ωH = 2.0 * PI * freqsHigh[i] / SAMPLE_RATE;
coeffsHigh[i] = 2.0 * cos(ωH);
}
}
void loop() {
// reset Goertzel states
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
sLow_prev[i] = sLow_prev2[i] = 0;
sHigh_prev[i] = sHigh_prev2[i] = 0;
}
unsigned long startMicros = micros();
// collect N samples
for (uint16_t n = 0; n < N; n++) {
while (micros() - startMicros < (unsigned long)(n * (1000000.0 / SAMPLE_RATE)));
float sample = (analogRead(A0) / 1024.0) - 0.5;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
float s = sample + coeffsLow[i] * sLow_prev[i] - sLow_prev2[i];
sLow_prev2[i] = sLow_prev[i];
sLow_prev[i] = s;
s = sample + coeffsHigh[i] * sHigh_prev[i] - sHigh_prev2[i];
sHigh_prev2[i] = sHigh_prev[i];
sHigh_prev[i] = s;
}
}
// compute magnitudes
float magLow[4], magHigh[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
magLow[i] = sLow_prev2[i]*sLow_prev2[i] + sLow_prev[i]*sLow_prev[i]
- coeffsLow[i]*sLow_prev[i]*sLow_prev2[i];
magHigh[i] = sHigh_prev2[i]*sHigh_prev2[i] + sHigh_prev[i]*sHigh_prev[i]
- coeffsHigh[i]*sHigh_prev[i]*sHigh_prev2[i];
}
// find best and second-best bins
int bestLowIdx=-1, bestHighIdx=-1;
float bestLow=0, secondLow=0, bestHigh=0, secondHigh=0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
float v = magLow[i];
if (v > bestLow) { secondLow = bestLow; bestLow = v; bestLowIdx = i; }
else if (v > secondLow) secondLow = v;
v = magHigh[i];
if (v > bestHigh) { secondHigh = bestHigh; bestHigh = v; bestHighIdx = i; }
else if (v > secondHigh) secondHigh = v;
}
// threshold + ratio test
const float THRESH = 0.01;
const float RATIO = 5.0; // require best > RATIO * second-best
bool validLow = (bestLow > THRESH && bestLow > secondLow * RATIO);
bool validHigh = (bestHigh > THRESH && bestHigh > secondHigh * RATIO);
if (validLow && validHigh) {
char digit = dtmfMap[bestLowIdx][bestHighIdx];
if (digit != lastDigit) {
Serial.print("DTMF: ");
Serial.println(digit);
lastDigit = digit;
}
} else {
lastDigit = '\0';
}
delay(10);
}
Not anywhere near as impressive as Linus’s C64 work, but I was able to get the hex dump data on the serial monitor. I did want to include the process of decoding DTMF with the Arduino Uno using the MT8870 module. It isn’t as elegant as a native ESP8266 approach, more hardware, pins used, and overall costs. The examples I found online contained mistakes so here is the code that worked for me.
/*Define input pins for DTMF Decoder pins connection */
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(8, INPUT); // connect to Std pin
pinMode(9, INPUT); // connect to Q4 pin
pinMode(10, INPUT); // connect to Q3 pin
pinMode(11, INPUT); // connect to Q2 pin
pinMode(12, INPUT); // connect to Q1 pin
}
void loop() {
uint8_t number_pressed;
bool signal ;
signal = digitalRead(8);
if(signal == HIGH) /* If new pin pressed */
{
delay(250);
number_pressed = ( 0x00 | (digitalRead(9)<<0) | (digitalRead(10)<<1) | (digitalRead(11)<<2) | (digitalRead(12)<<3) );
switch (number_pressed)
{
case 0x01:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = 1");
break;
case 0x02:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = 2");
break;
case 0x03:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = 3");
break;
case 0x04:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = 4");
break;
case 0x05:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = 5");
break;
case 0x06:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = 6");
break;
case 0x07:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = 7");
break;
case 0x08:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = 8");
break;
case 0x09:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = 9");
break;
case 0x0A:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = 0");
break;
case 0x0B:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = *");
break;
case 0x0C:
Serial.println("Button Pressed = #");
break;
}
}
}
Decoding Morse code is becoming a lost art done by humans. It and DTMF are primarily used between machines for connections that have extreme hardware and bandwidth limitations. It has a rich history as the foundation for our modern digital age. I would recommend further reading on the subject if this interests you.
Morse code – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morse_code
The Morse Code (CW) Radio Center of NW7US – https://cw.hfradio.org/
DTMF signaling – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DTMF_signaling
Goertzel algorithm – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Goertzel_algorithm